Introduction
Improving the Lifetime Value (CLV) in eCommerce is crucial, and customer segmentation plays a vital role in this endeavor. This article, intended for eCommerce marketing professionals working on enhancing CLV, explains four types of customer segmentation and the four 'R' conditions of a good customer segment.
Overview of Customer Segmentation and its Benefits for eCommerce Marketers
What is Customer Segmentation?
Customer segmentation involves categorizing customers based on their characteristics and behaviors, thereby classifying them into groups with similar needs. The main types of customer segmentation include demographic segmentation using "demographic variables", psychological segmentation using "psychological variables", geographic segmentation using "geographic variables", and behavioral segmentation using "behavioral variables".
Enhancing Customer Resolution and Optimizing Marketing Measures through Customer Segmentation
In today's world, where consumer needs are increasingly diversified, it's challenging for eCommerce businesses, which inherently lack face-to-face interactions, to offer personalized customer experiences. By utilizing data and effectively segmenting customers, marketers can enhance customer resolution.
Understanding the needs, purchase intentions, and buying trends of different types of customers allows for optimization of marketing strategies on a segment-by-segment basis.
For eCommerce Marketers, Customer Segmentation is the Ideal CRM Layer
In recent years, more eCommerce operators have introduced CRM tools to provide optimal support tailored to each customer. While it's essential to engage with each customer as if in face-to-face sales, from a "marketing professional" perspective, looking at each customer's data might be overly detailed.
For eCommerce marketers, the most appropriate layer of customer management is "customer segmentation."
Why is Customer Segmentation Important for Improving CLV in eCommerce?
Optimize Various Measures Aimed at Enhancing CLV
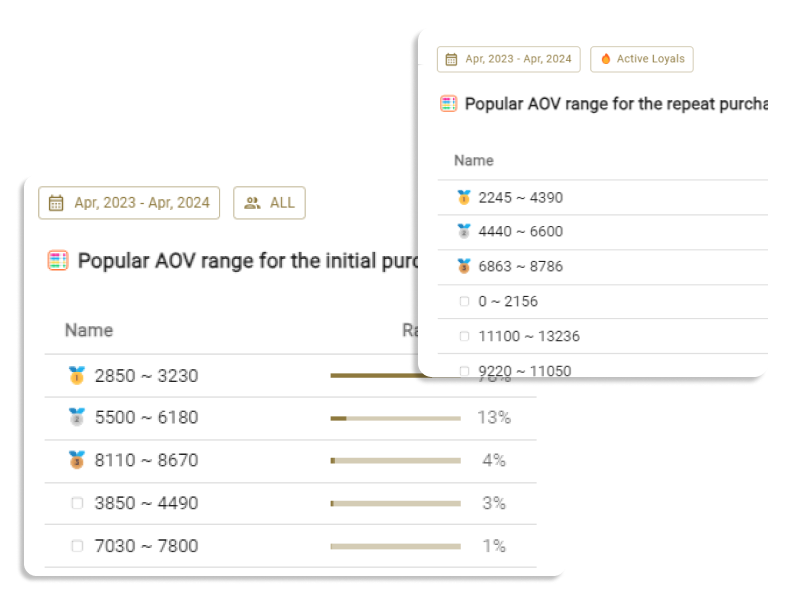
If we go back to the definition of CLV, it can be broken down into elements like "average order amount", "purchase frequency", and "customer lifespan". Simply put, by improving each of these metrics, CLV will increase. To raise the "average purchase price", you can utilize upselling or cross-selling, "purchase frequency" can be enhanced with effective email marketing, and measures like loyalty programs or introducing subscriptions can extend the "customer lifespan".
However, if customer purchasing intentions, needs, and preferences differ, the elements to focus on for enhancing CLV and the necessary actions will also vary.
For instance, even in an eCommerce store for baby and children's goods, customers purchasing mainly toys will differ from those buying consumables like diapers in terms of average order amounts and purchase frequencies. Customers who buy toys might continue to do so until their child reaches a certain age, whereas those buying diapers will likely have a customer lifespan of just a few months to a few years. In this case, the marketing strategies to enhance CLV would naturally differ for customers primarily purchasing toys versus those mainly buying diapers.
By appropriately segmenting eCommerce customers into the right customer segments, you can optimize marketing measures for each segment to improve CLV.
Enhancing Targeting Precision
The term "segmentation" is often described as one of the elements in "STP". STP stands for Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning, and it is a fundamental framework in marketing.
While STP is often used in the context of new market development, in marketing aimed at existing customers with the goal of improving CLV, the skillfulness of segmentation is vital as a prerequisite for precise targeting.
Only by appropriately segmenting a large number of existing customers can you discuss "how to allocate limited marketing resources to which segment" and "which segments should be focused on or nurtured now", enabling the implementation of high ROI measures.
Personalize Communication and Enhance Loyalty
By the eCommerce business side implementing marketing measures linked to appropriate customer segments based on needs, the content of promotions or messages can be tailored more closely to customer preferences and needs.
From the receiver's perspective, if the message content is closer to one's own preferences, one would be inclined to read it with interest. Feeling that "the brand understands my preferences" can lead to increased trust, intimacy, and loyalty towards the brand.
Thus, by appropriately conducting customer segmentation, not only can you optimize efforts towards various measures for improving CLV, but you can also increase the ROI of marketing measures through effective targeting and enhance customer loyalty.
4+1 Types of Customer Segmentation
The representative customer segments include four types: demographic segment, geographic segment, behavioral segment, and psychological segment. Also, as a derivative of the behavioral segment, there's the RFM segmentation framework commonly used in eCommerce. First, let's briefly discuss each of these.
Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation is a method of customer segmentation based on attribute data such as age, gender, family composition, income level, occupation, and education. Demographic data is useful as a proxy variable to identify the needs associated with each customer's life cycle. For more details, please refer to the article below.
Reference article:
Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation refers to creating segments based on geographic data, such as the country or region where customers reside, taking into account regional trends, preferences, and needs. In e-commerce, geographic data can be effectively used as a proxy for the customer's lifestyle. For more details, please refer to the article below.
Reference article:
Behavioral Segmentation
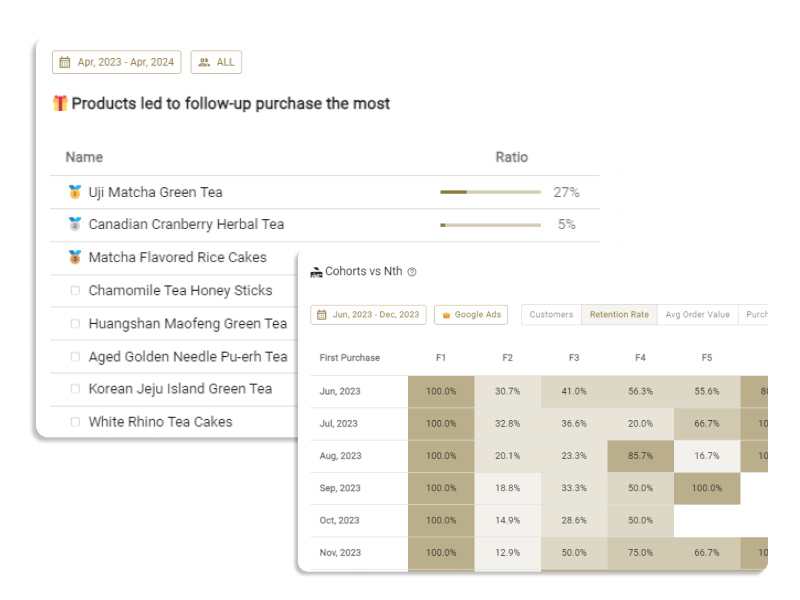
Behavioral segmentation in e-commerce is a method of categorizing customers based on common behavior patterns such as site visit history, purchase history of products, product usage, and engagement. Behavioral segmentation allows for the inference of the motives behind customer actions, revealing hidden needs and purchasing intentions, and enables targeted marketing measures. For more details, please refer to the article below.
Reference article:
Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation is a technique that focuses on psychological factors such as preferences, lifestyle, attitudes, values, and purchasing motives to segment customers. It's easy to understand psychographic segmentation as adding psychological interpretations to objective data groups such as demographic and geographic data, as well as behavioral history. For more details, please refer to the article below.
Reference article:
[Advanced] RFM Segmentation
RFM analysis (or RFM segmentation) is a type of "behavioral segmentation." RFM analysis breaks down customer purchasing behavior into three main elements: Recency (days since the last purchase), Frequency (number of purchases), and Monetary (total purchase amount). The acronym RFM is widely used based on the initials of these elements.
By scoring customers from an RFM perspective and segmenting them accordingly, it becomes possible to implement marketing measures tailored to the purchasing behavior of each segment. For more details, please refer to the article below.
Reference article:
Understanding the Four Types of Segmentation
Generally speaking, the explanation goes up to the point that there are four types of segments: "demographic segment," "geographic segment," "behavioral segment," and "psychological segment."
From here, incorporating the viewpoint of the author (ECPower Inc.), we will explain how eCommerce marketers should combine the four segmentations in their practical work.
"Psychographic Segment" is the Most Fundamental and Important, but Difficult to Collect Data
First and foremost, the four types of segmentation should not be treated in parallel.
Among these, the most important is the "psychological segment." In other words, understanding what customers like, what they need, and why and with what purpose they purchase is fundamental to all marketing measures.
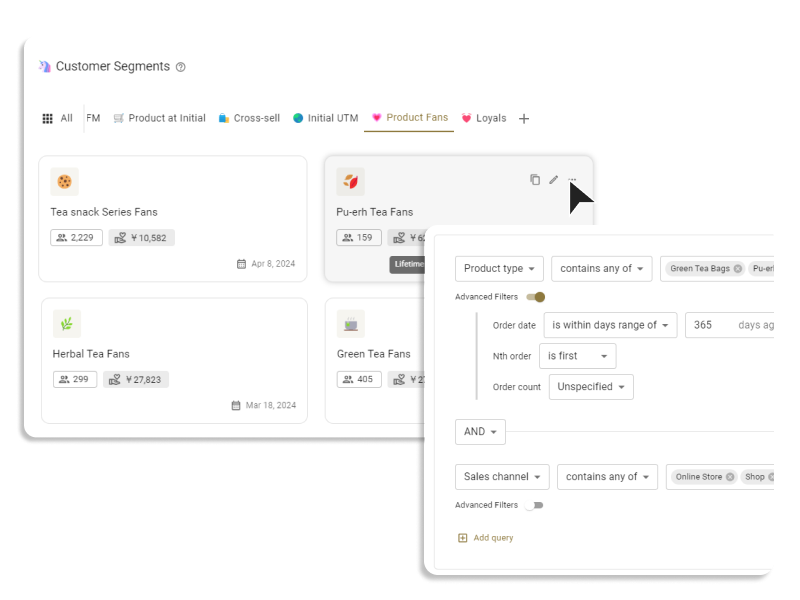
The essence of customer segmentation is to categorize customers with similar needs. Therefore, mechanically creating segments based on age and gender isn't practical. We, the customer segmentation tool ECPower, believes that a segmentation that effectively reveals psychological needs is the most essential "visible segment."
However, obtaining data that directly represents a customer's psychology is very challenging. For instance, it's not realistic to ask every customer, "What do you like?", "What are your needs?", or "What kind of values and lifestyle do you have?" through a survey.
Especially in the B2C domain, many people cannot verbalize their true needs. Even if a survey is conducted, the results might be off the mark.
Using Behavioral Data to Infer Psychographic Elements is a Practical Approach
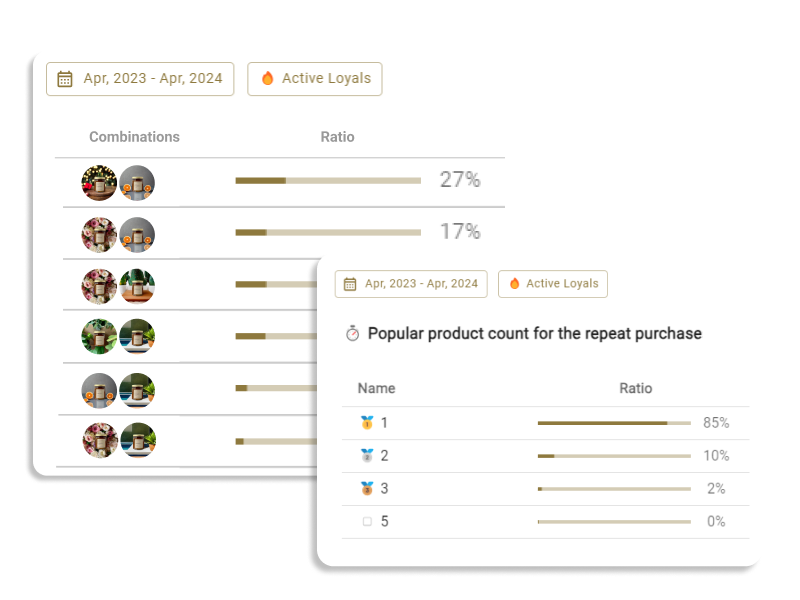
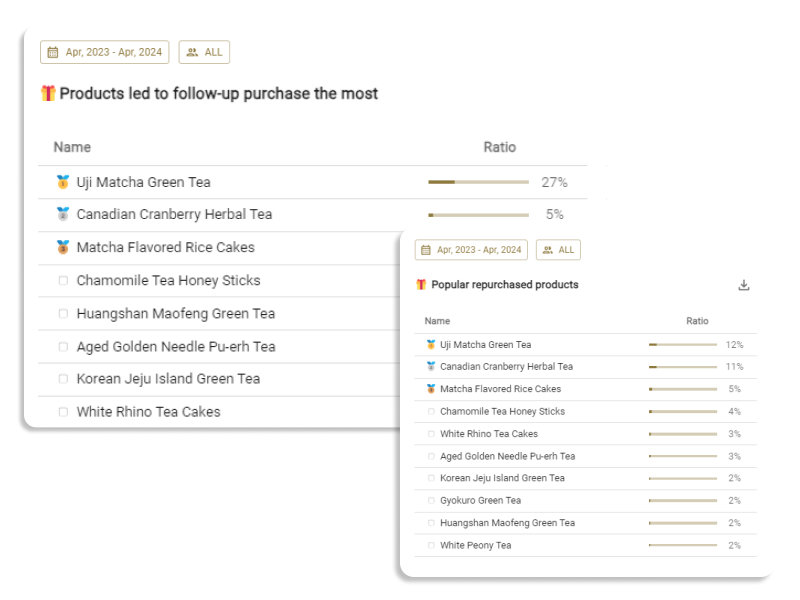
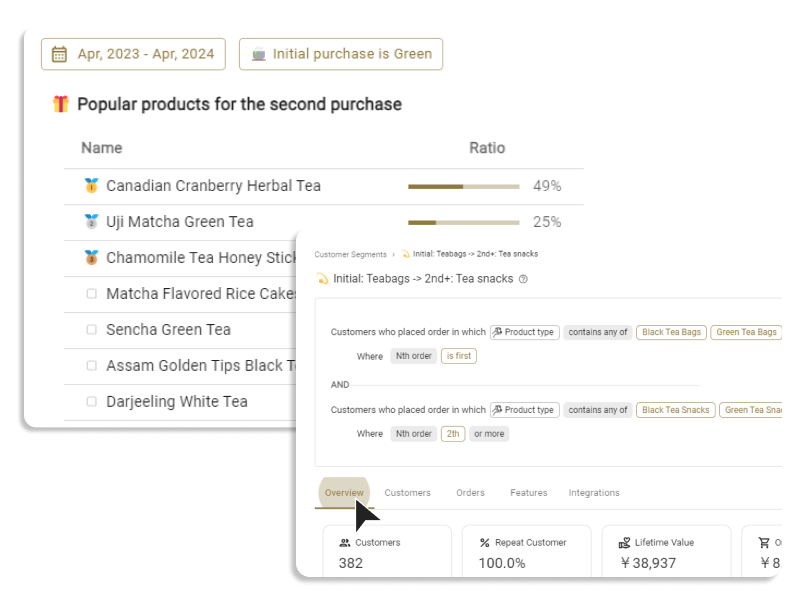
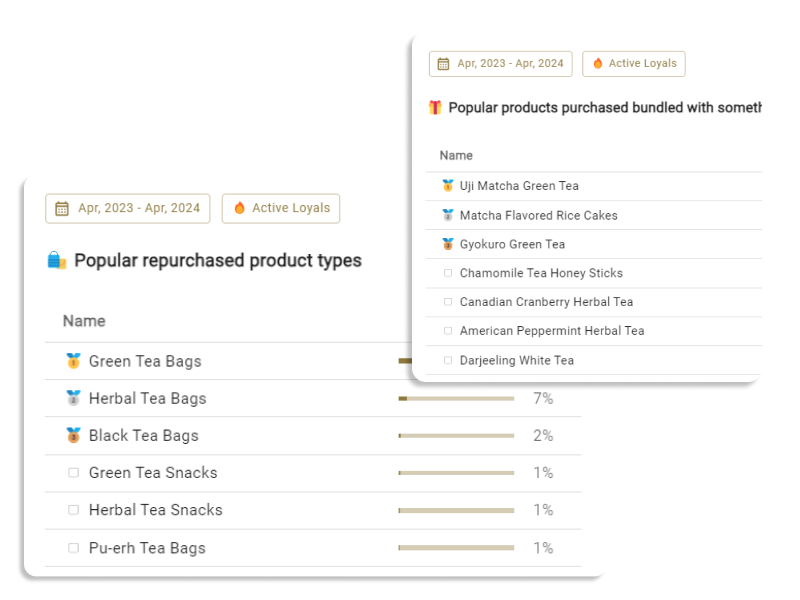
A customer's psychology manifests in their behavior. From products viewed on a site, products added to the cart, and actual purchased products and their combinations, one can infer a customer's preferences and needs. A customer who often purchases new products might have psychological characteristics that seek diversity and novelty.
Most eCommerce operators already possess customer behavioral data, such as order history, site visit data, and data related to email marketing conversion. Therefore, a most practical approach is to conduct behavioral segmentation and ascribe "psychological meanings" to it.
Moreover, while demographic and geographic data are static, behavioral data is updated in real-time, offering an advantage in grasping the latest psychological state.
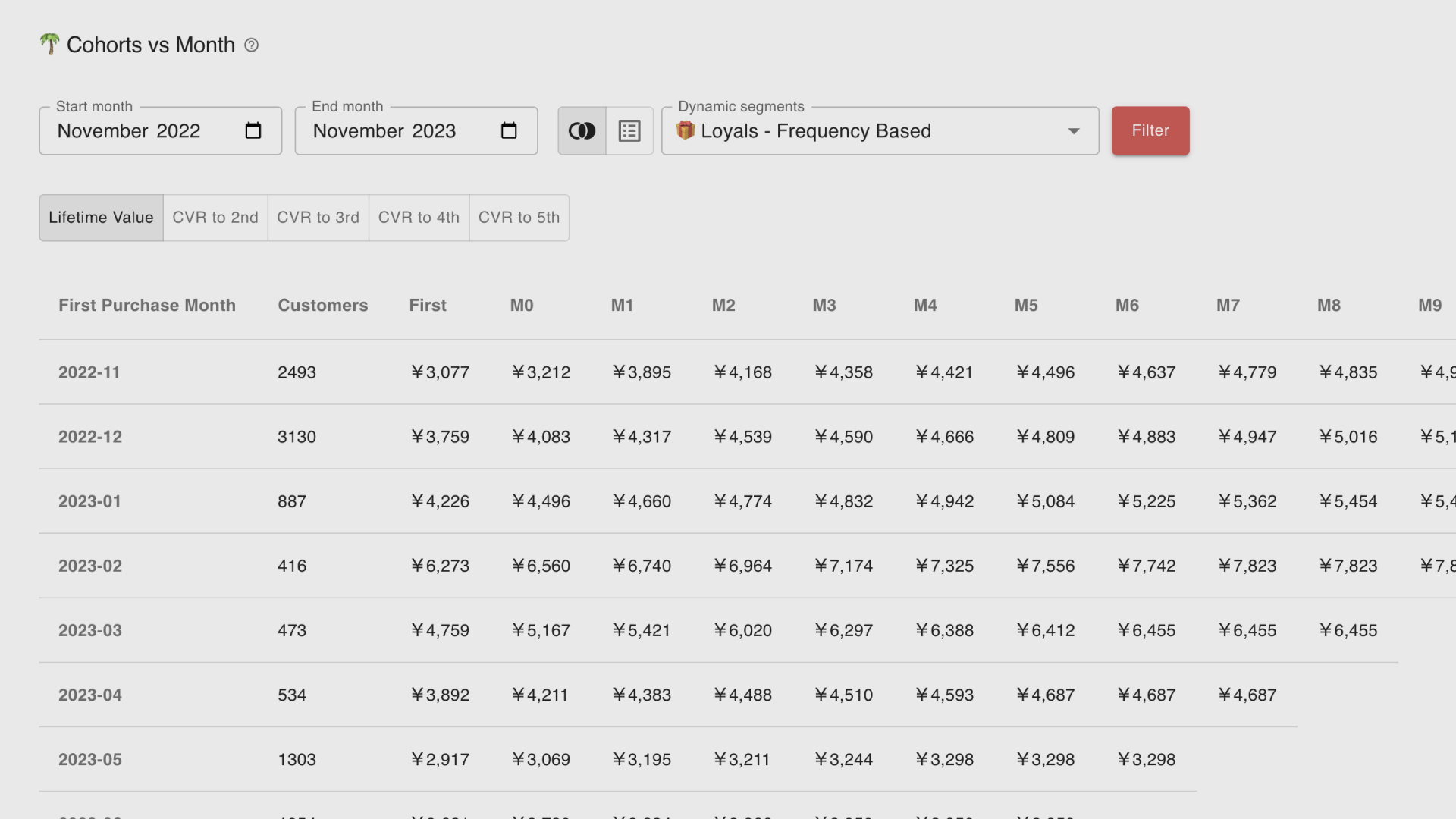
Improving CLV means building a long-term relationship with a customer. Throughout the long customer journey, a customer's psychological state changes daily through touchpoints like product purchasing, marketing promotions, and support communications. It's crucial not just to define a segment once but to revisit customer segments dynamically by reflecting the latest behavioral data.
Use Demographic and Geographic Data as Proxy Variables for Needs Related to Lifestyle and Life Stage
Of course, segmentation using geographic and demographic data is essential. However, blindly creating segments based on age or prefecture isn't a wise approach.
For example, you can view geographic data as a proxy variable for needs related to "lifestyle." As one perspective, what if you divide it into two segments: the so-called urban areas and regions that aren't much urbanized? By doing so, you can start to imagine differences in "lifestyle", like the average number of household members, car ownership, type of housing, and how leisure time is spent.
Furthermore, demographic data can be easily understood when viewed as a proxy variable for needs related to "life stage." By utilizing data like gender, age, current occupation, and income level, you can estimate the needs associated with each step in an individual's life. For instance, for products focused on life events like marriage or childbirth, you can create segments using demographic data, targeting those in their 20s to 30s.
How to Understand the Four Types of Segmentation
Creating a "psychological segment" that directly represents customer needs, preferences, and purchasing intentions is of utmost importance. However, since it's challenging to obtain direct data, it's vital to analyze behavioral data in real-time to infer needs, attitudes, and psychological states or use static demographic and geographic data to deduce lifestyles and lifecycle needs.
Perhaps an ideal and practical customer segmentation in EC would be to wisely combine "behavioral segment," "demographic segment," and "geographic segment," and then ascribe psychological meanings to these customer segments.
Essential Conditions for Excellent Customer Segments: "4R"
To conclude, we'll touch upon the conditions for a good customer segment. The conditions for effective segmentation are often called "4R", standing for Rank (can priorities be set?), Realistic (is there a valid scale?), Reach (is it accessible?), and Response (can the results be measured?).
Rank (Can Priorities Be Set?)
When considering targeting, it's necessary that the created customer segments can be prioritized based on factors like CLV, profitability, and maintenance costs.
Realistic (Is There a Valid Scale?)
If a segment is too small, the return on marketing measures might be too low. Depending on the size of the eCommerce store and the purpose of segmentation, a segment size of at least around 100 people would be ideal.
Reach (Is it Accessible?)
This aspect looks at whether access to the segment is possible. For instance, if email is the primary communication method, the actual number of customers that can be reached might be extremely limited due to email delivery refusals (opt-outs).
Response (Can It Be Measured?)
This perspective assesses whether the reaction to marketing measures implemented for a segment can be measured. For standard email delivery tools, tracking metrics like open rates and click rates is possible. Ideally, it would be possible to measure all the way from promotional measures to sales. However, it's essential first to consider the communication methods currently in use and determine whether their effectiveness can be measured.
Conclusion
Customer segmentation can enhance customer resolution and optimize marketing measures. Additionally, by personalizing communication, it contributes to enhancing CLV.
Creating a "psychological segment" that directly represents customer needs, preferences, and purchasing intentions is of utmost importance. However, since obtaining direct data can be challenging, it's crucial to analyze behavioral data in real-time to infer needs, attitudes, and psychological states or utilize static demographic and geographic data to deduce lifestyles and lifecycle needs.
When creating customer segments, it's essential to consider perspectives such as whether priorities can be set, whether there's a valid scale, whether it's accessible, and whether results can be measured.
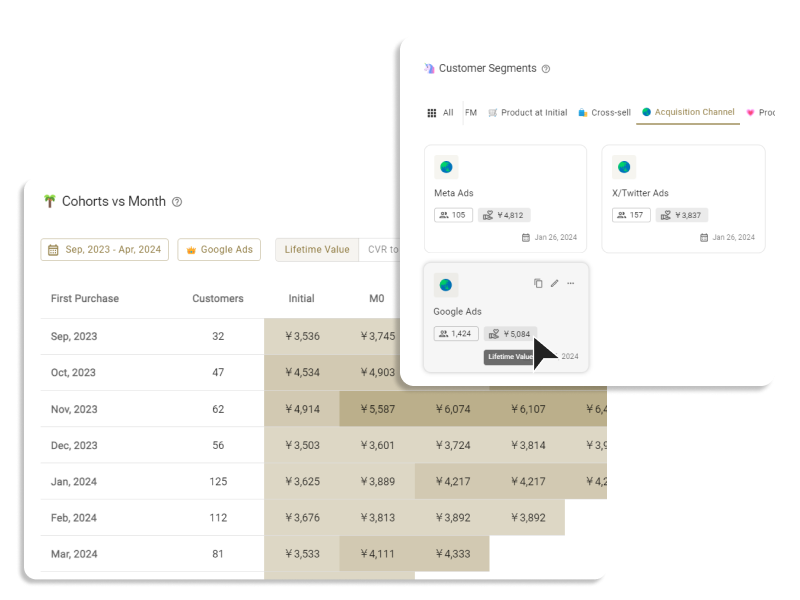
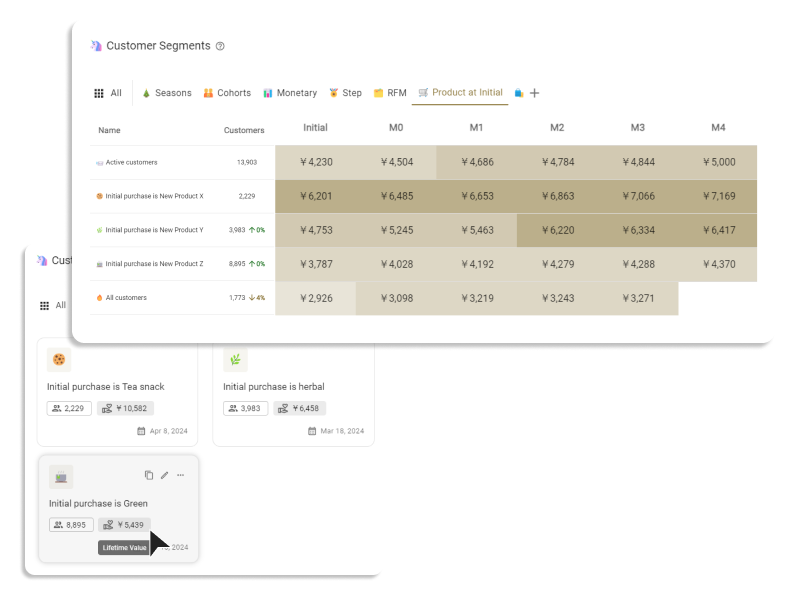
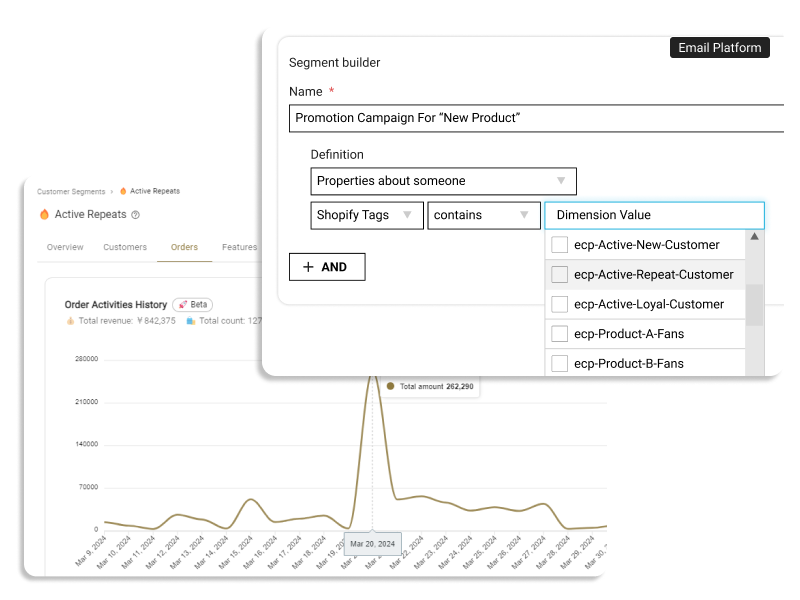
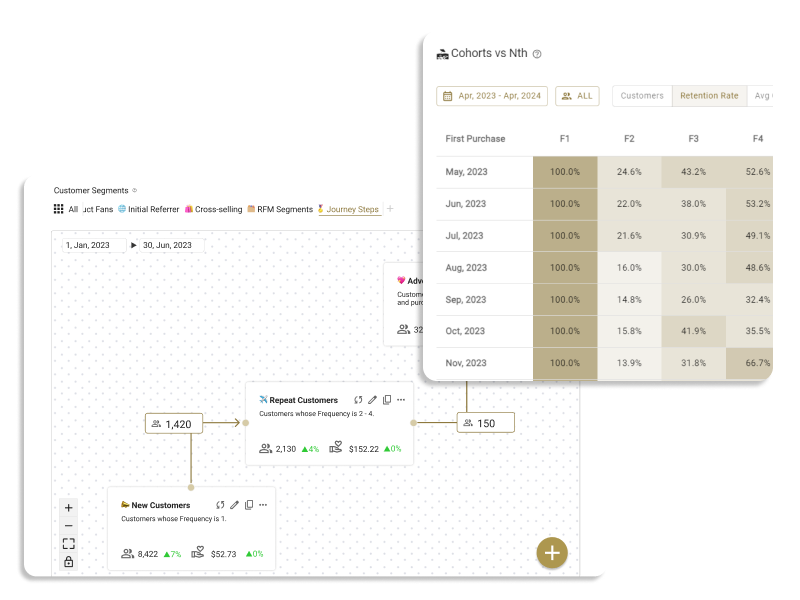
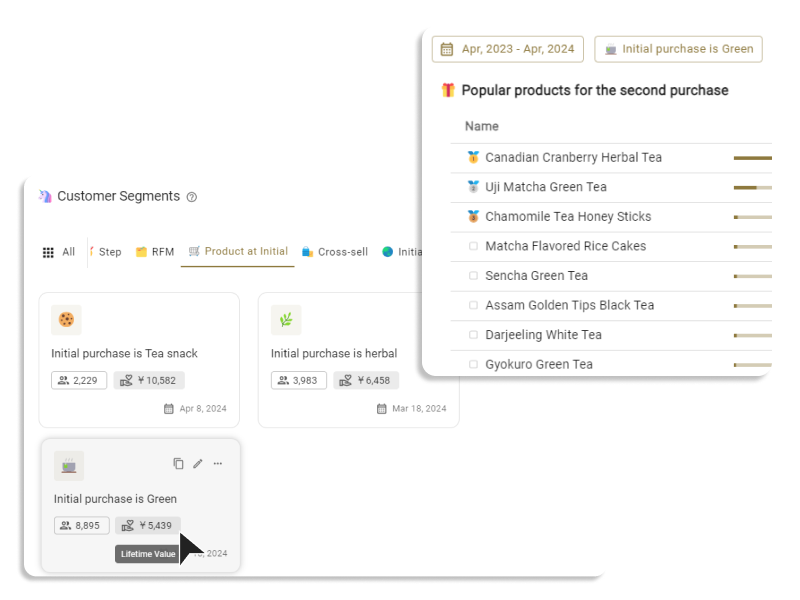
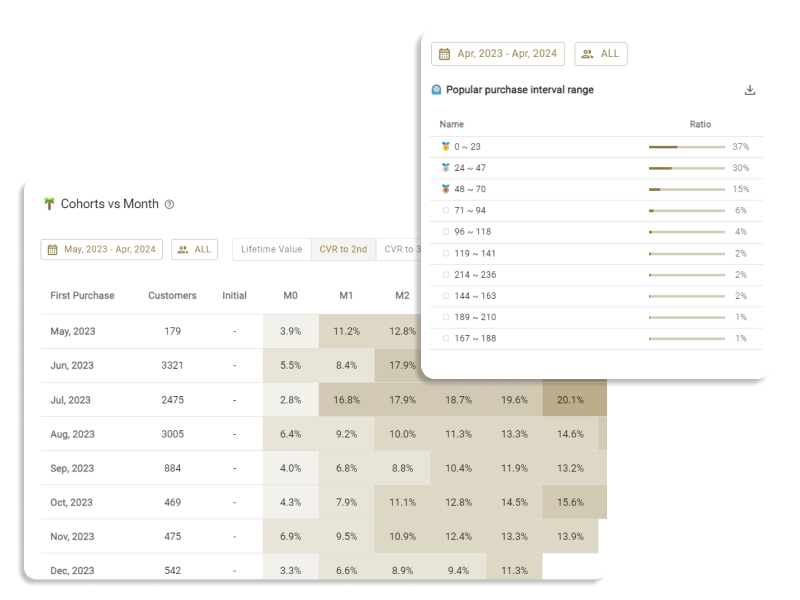
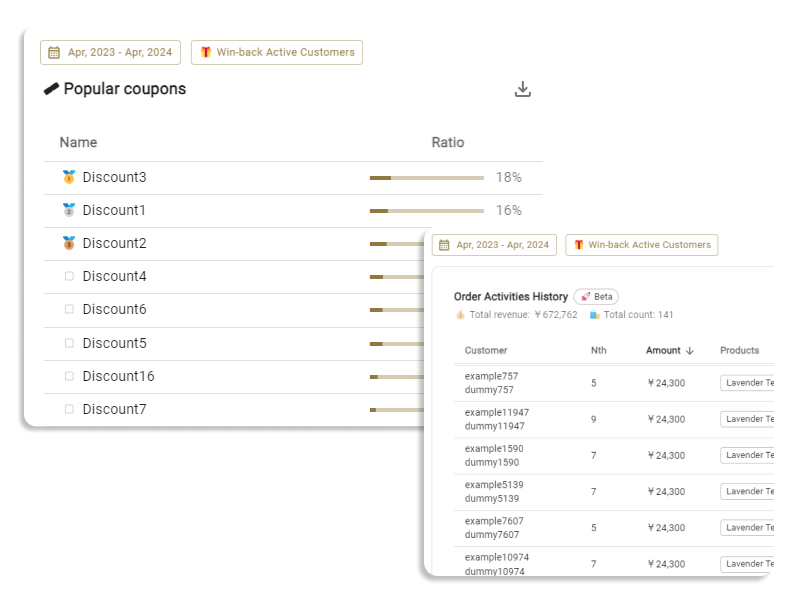
The customer segmentation tool ECPower enables the creation of "visible" segments using behavioral data, without requiring any coding. You can manage and compare KPIs like CLV, average order amount, and purchase intervals by segment, quickly grasping essential segments. Furthermore, by seamlessly integrating with currently used MA & CRM tools, it's possible to measure the effects of marketing measures implemented for segments in terms of sales.
If you're interested, please also check our product site.