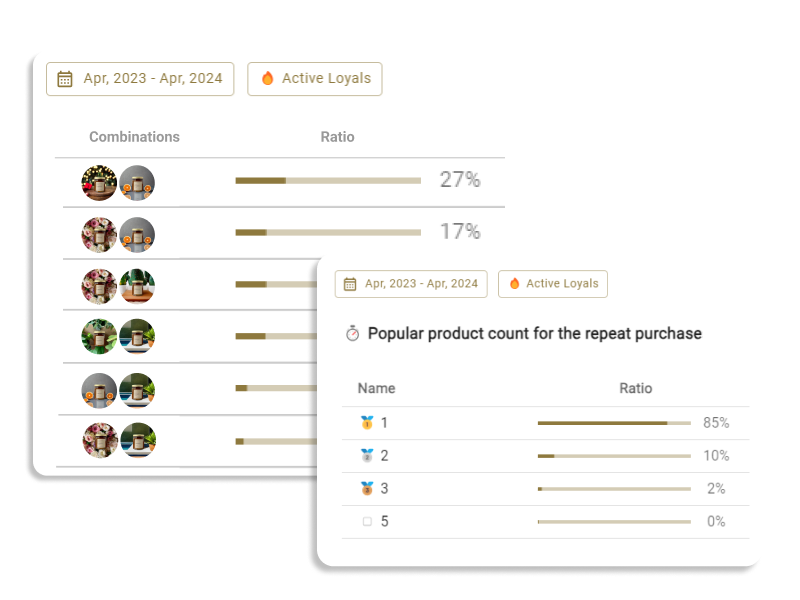
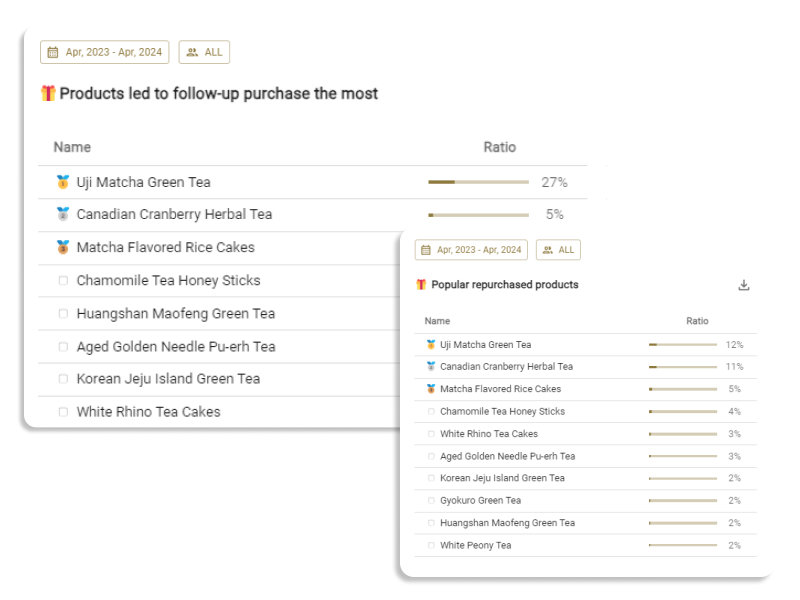
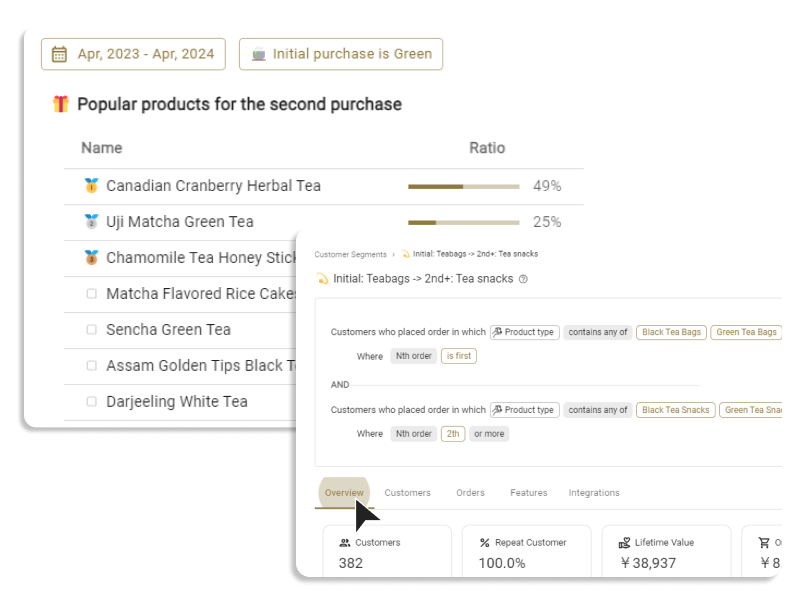
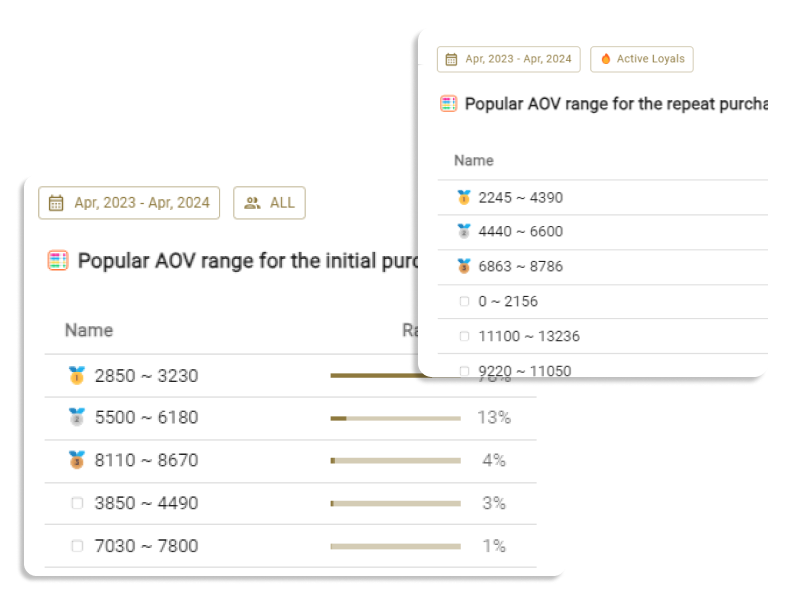
Introduction
One of the methods of customer segmentation is "geographical segmentation." In eCommerce, it is beneficial to consider it as a proxy variable for "lifestyle." This article is aimed at eCommerce marketers who are working on improving CLV, and it explains the overview and application methods of geographical segmentation.
What is Customer Segmentation in eCommerce?
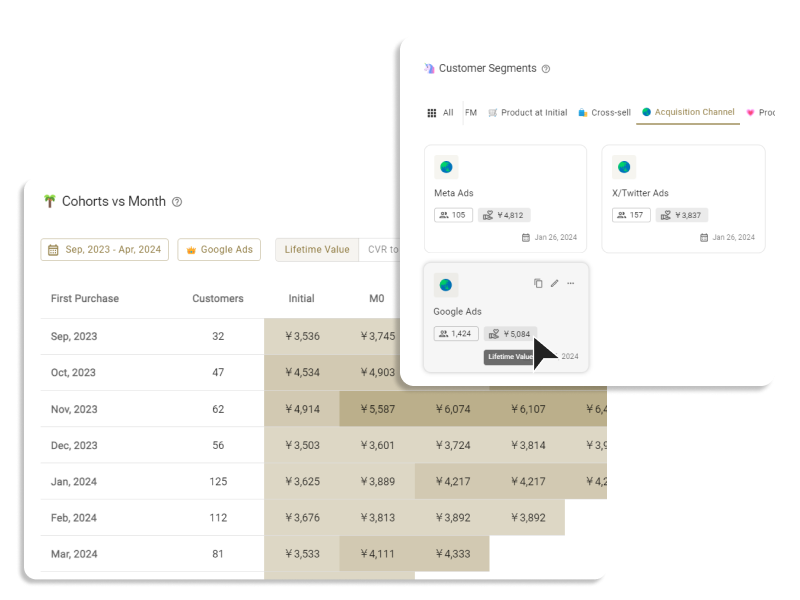
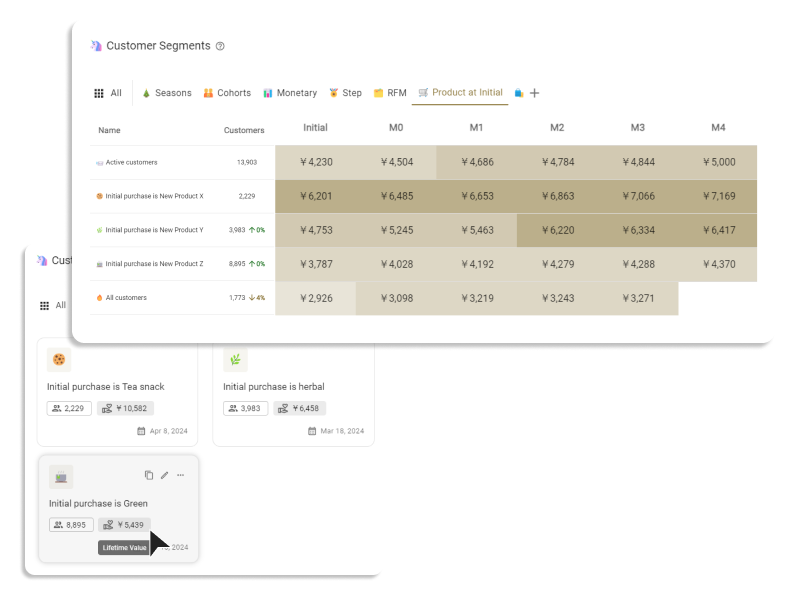
Customer segmentation in eCommerce refers to categorizing customers based on their characteristics and behaviors. The main types of customer segmentation include attribute segments (age, gender), psychological segments, geographical segments (country of residence, place of residence), and behavioral segments (purchase history, actions on the site, etc.).
eCommerce businesses can understand the needs, purchase intentions, and purchasing trends of different types of customers through customer segmentation, enhancing customer resolution and implementing effective marketing measures.
What is Geographical Segmentation?
First, let's explain the general geographical segmentation, not limited to eCommerce.
Geographical segmentation refers to creating segments based on geographical data, taking into account regional trends, preferences, and needs.
Since regions differ in climate, weather, culture, traditions, economic factors, and infrastructure development, depending on the type of product, there may be different needs depending on the place of residence. By performing geographical segmentation, one can utilize geographical data as a proxy variable for these needs, reflecting in the opening of physical stores, placing advertisements, and regional product variations.
Climate and Weather Patterns
Globally, there are significant differences in climate and weather patterns depending on the region, which can greatly influence the needs and preferences of residents. While it's an essential consideration for companies operating worldwide, in Japan too, there are patterns such as areas with high rainfall or relatively warm regions. For example, in cold areas, there's an expected high demand for clothing with high functionality in cold protection.
Cultural, Religious, and Traditional Differences
Regions differ significantly in terms of culture and traditions, which can influence consumer preferences and behaviors. On a national level, different religious backgrounds in various regions might necessitate adjustments to the product itself or its promotion. For instance, it is well-known that food companies in Japan adjust the flavoring of the same product depending on whether it's intended for the Kanto or Kansai region.
Economic Level
Economic levels, such as income levels and living expenses, can vary based on geographical location. For example, residents in affluent areas might have different purchasing habits and preferences compared to customers in less economically privileged regions.
Location Characteristics
Especially crucial for companies with physical stores are the characteristics of the location, such as the purpose of the city block or transportation infrastructure. For instance, convenience stores adjust their product lineup depending on whether they are located in office districts or residential areas.
How to Utilize Geographical Segmentation in eCommerce
Now, let's explain how to practically utilize geographical segmentation in the eCommerce business.
If you are operating on a global scale, you might already be conducting marketing considering factors specific to each country, such as climate, culture, religion, and economy. On the other hand, for businesses catering to a domestic market, recommendations like "segmentation should be done by prefecture" might not resonate as clearly.
The basic idea behind customer segmentation is to "create clusters of customers with the same needs." Therefore, if we view geographical data as a "proxy variable for lifestyle," it might become more manageable for eCommerce companies. Let's explain using several perspectives.
Segmenting Urban Areas vs. Others
One approach is to use customer residence data to segment into two categories: the so-called urban areas and areas that are not heavily urbanized. By doing this, one can imagine the differences in "lifestyle" such as average household size, private car ownership, whether living in a single-family home or an apartment, and how leisure time is spent.
For instance, if it's an eCommerce store for gifts, targeting the customer segment in urban areas—where many live away from their parent's household—you could consider marketing promotions like proposing e-gifts (Note: a method to gift without meeting in person) for occasions like Father's Day or Mother's Day.
Segmenting Based on the location of offline stores
Another approach is to analyze and segment based on the number, product range, and accessibility of physical stores that offer products similar to your eCommerce platform.
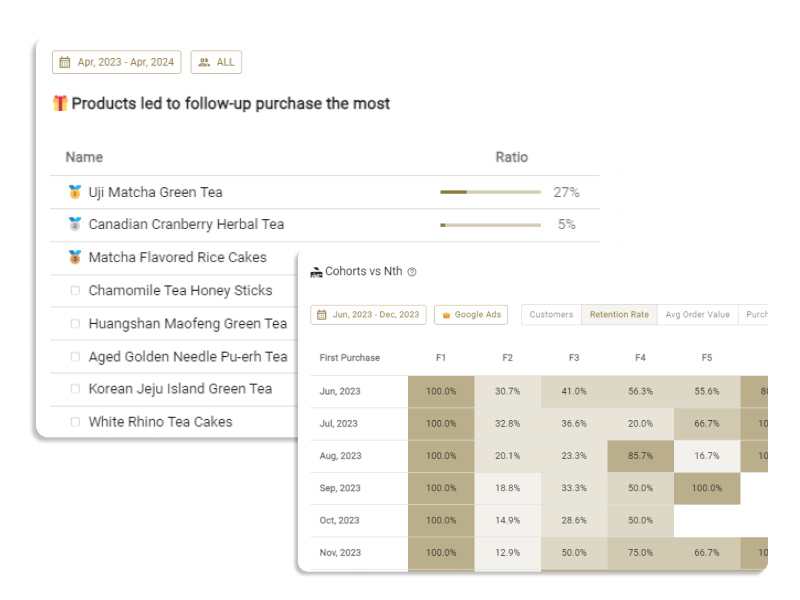
For example, in areas with few store options, limited product variety, or where access to physical stores is inconvenient, the importance of purchasing products via eCommerce becomes relatively higher. This could lead to the hypothesis that such areas might be more inclined towards repeat purchases.
Instead of mechanically segmenting by prefectures, segmenting in a way that allows for imagining the "lifestyle" of customers can provide meaningful insights for marketing.
Conclusion
While understanding a customer's lifestyle is indeed a critical perspective in marketing, in the case of eCommerce, it's incredibly challenging to grasp the lifestyle of individual customers. Even if post-purchase surveys are utilized, the hurdle to collect data that can be directly applied for segmentation is arguably high.